10+ Autism Genetic Testing Secrets For Early Detection

Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a complex neurological disorder that affects communication, social interaction, and behavior. With the advancements in genetic testing, early detection of autism has become more feasible, enabling timely interventions and improved outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the realm of autism genetic testing, exploring the secrets and benefits of early detection.
Introduction to Autism Genetic Testing
Genetic testing for autism involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify potential genetic mutations or variations that may contribute to the development of autism. This type of testing can be particularly useful for families with a history of autism, as it can help identify genetic risks and enable early intervention. Early detection is crucial, as it allows for the implementation of targeted therapies and interventions, which can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with autism.
Types of Autism Genetic Testing
There are several types of genetic tests available for autism, including:
- Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA): This test examines the entire genome for copy number variations (CNVs) and other chromosomal abnormalities.
- Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES): This test analyzes the protein-coding regions of the genome to identify potential mutations.
- Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS): This test provides a comprehensive analysis of the entire genome, including non-coding regions.
Each of these tests has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of test depends on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. Genetic counseling is essential to help families understand the results and implications of these tests.
Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection of autism through genetic testing can have a significant impact on the individual’s development and quality of life. Some of the benefits of early detection include:
- Targeted interventions: Early detection enables the implementation of targeted therapies and interventions, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and speech therapy, which can help improve communication and social skills.
- Personalized treatment plans: Genetic testing can help identify specific genetic mutations or variations, allowing for the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s unique needs.
- Increased awareness and understanding: Early detection can help families and caregivers better understand the individual’s needs and behaviors, reducing stress and improving relationships.
By identifying genetic risks and enabling early intervention, genetic testing can play a critical role in improving outcomes for individuals with autism.
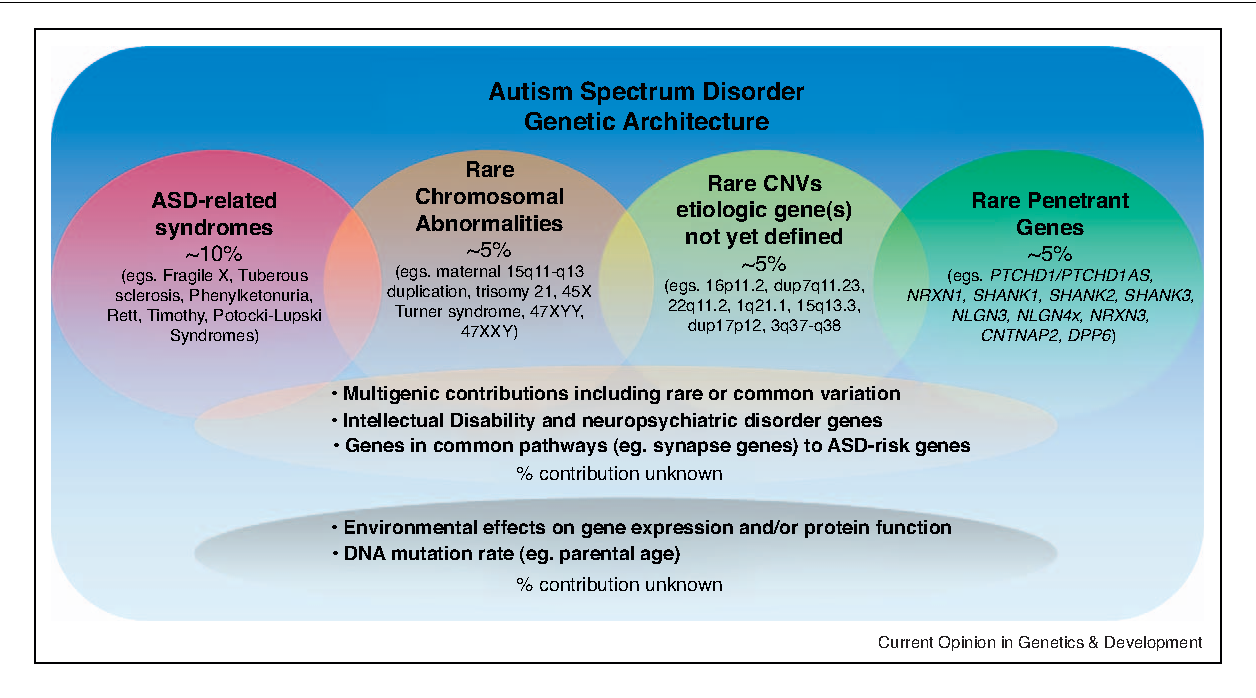
Genetic Mutations and Variations Associated with Autism
Research has identified several genetic mutations and variations that are associated with an increased risk of autism. Some of the most common include:
| Genetic Mutation/Variation | Associated Risk |
|---|---|
| SHANK3 mutation | Increased risk of autism and intellectual disability |
| TSC2 mutation | Increased risk of autism and tuberous sclerosis complex |
| 16p11.2 deletion | Increased risk of autism and developmental delay |
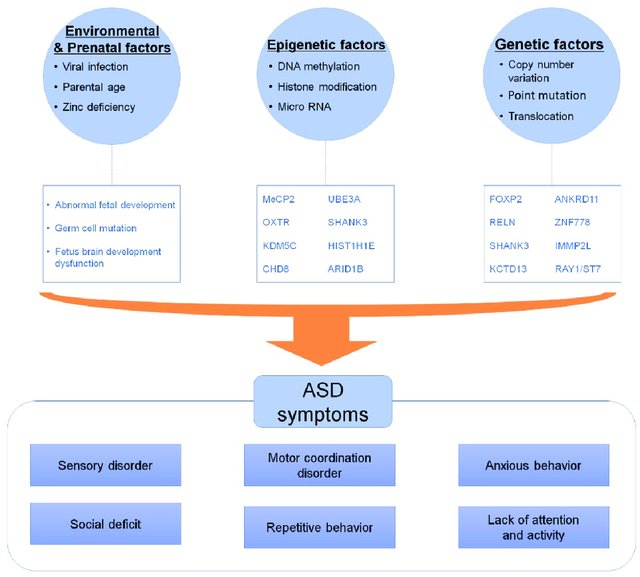
These genetic mutations and variations can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of autism and help guide treatment decisions.
Future Directions in Autism Genetic Testing
As genetic testing technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see significant advancements in the field of autism genetics. Some potential future directions include:
- Genomic sequencing: The use of genomic sequencing to analyze the entire genome and identify potential genetic mutations or variations.
- Epigenetic analysis: The study of epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, which can influence gene expression and contribute to autism.
- Gene editing technologies: The development of gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9, which may potentially be used to treat genetic disorders, including autism.
These emerging technologies hold promise for improving our understanding of autism genetics and enabling the development of more effective treatments.
What is the current accuracy of autism genetic testing?
+The current accuracy of autism genetic testing varies depending on the type of test and the individual's specific circumstances. However, most genetic tests can identify genetic mutations or variations associated with autism in approximately 10-20% of cases.
Can genetic testing predict the severity of autism?
+Currently, genetic testing cannot predict the severity of autism. However, research suggests that certain genetic mutations or variations may be associated with more severe symptoms or intellectual disability.
Is genetic testing for autism covered by insurance?
+Insurance coverage for genetic testing for autism varies depending on the individual's insurance plan and circumstances. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider or genetic counselor to determine the specifics of insurance coverage.
In conclusion, autism genetic testing has the potential to revolutionize the field of autism diagnosis and treatment. By identifying genetic mutations and variations associated with autism, genetic testing can enable early detection, targeted interventions, and personalized treatment plans. As research continues to advance, we can expect to see significant improvements in the accuracy and effectiveness of autism genetic testing.



