10 Shoulder Mri Insights For Accurate Diagnosis

The shoulder is a complex joint that is prone to various injuries and conditions, making accurate diagnosis crucial for effective treatment. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides detailed images of the shoulder joint, helping clinicians to identify and diagnose a range of conditions. In this article, we will delve into 10 key insights for accurate diagnosis using shoulder MRI, highlighting the importance of this imaging modality in clinical practice.
Introduction to Shoulder MRI
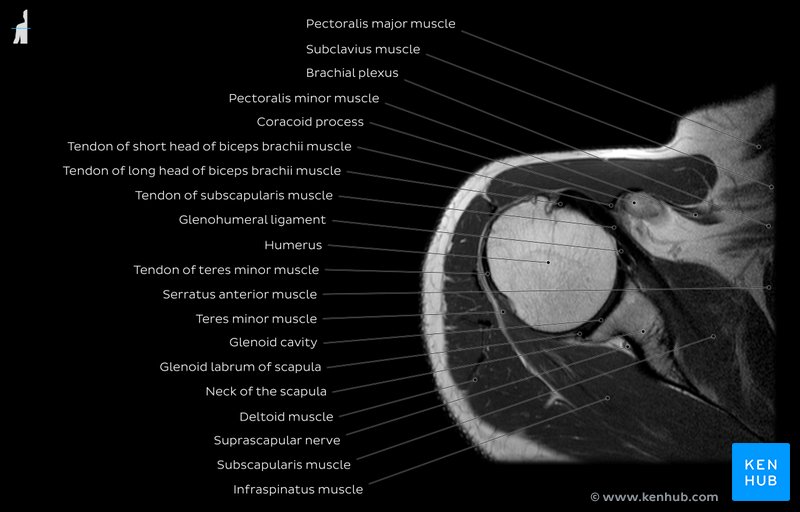
Shoulder MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce high-resolution images of the shoulder joint. The shoulder joint is composed of several structures, including bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles, which can be affected by various conditions such as rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, and adhesive capsulitis. Shoulder MRI is particularly useful for evaluating the soft tissues of the shoulder, including the rotator cuff, labrum, and cartilage.
Technical Considerations for Shoulder MRI
When performing a shoulder MRI, several technical considerations must be taken into account to ensure accurate diagnosis. These include the use of a high-field strength MRI machine, a dedicated shoulder coil, and a standardized imaging protocol. The imaging protocol should include a combination of T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and proton density-weighted sequences, which provide complementary information about the shoulder joint. Additionally, the use of intravenous contrast agents, such as gadolinium, may be necessary to evaluate certain conditions, such as rotator cuff tears or labral tears.
| Sequence | Weighting | Contrast |
|---|---|---|
| T1-weighted | Anatomical detail | Low |
| T2-weighted | Fluid-sensitive | High |
| Proton density-weighted | Cartilage evaluation | Intermediate |
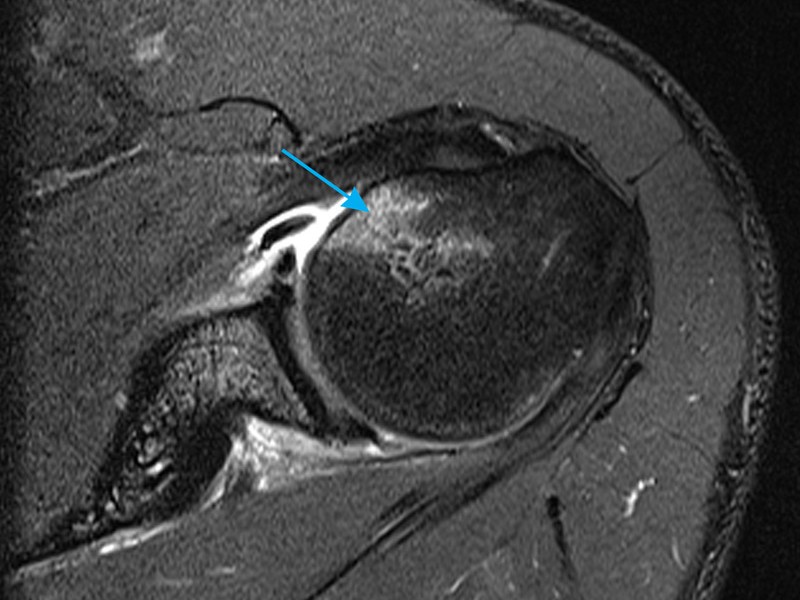
Insights for Accurate Diagnosis
The following 10 insights are essential for accurate diagnosis using shoulder MRI:
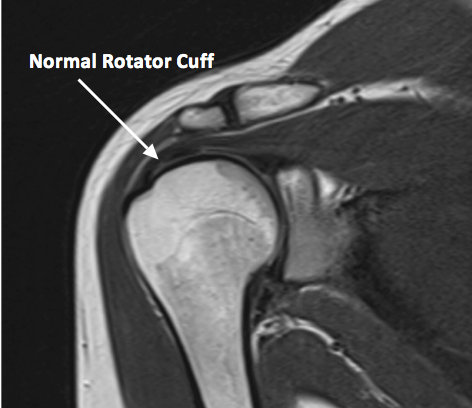
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Shoulder MRI is highly sensitive for detecting rotator cuff tears, which are common in patients with shoulder pain and weakness. The imaging findings of a rotator cuff tear include a focal disruption of the tendon, with or without retraction of the torn tendon.
- Shoulder Impingement: Shoulder impingement occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff are compressed against the acromion, leading to inflammation and pain. Shoulder MRI can detect the signs of shoulder impingement, including thickening of the subacromial bursa and sclerosis of the acromion.
- Labral Tears: The labrum is a cartilaginous structure that surrounds the glenoid fossa, and labral tears can occur due to trauma or degenerative changes. Shoulder MRI can detect labral tears, which appear as a linear defect in the labrum, with or without displacement of the torn fragment.
- Adhesive Capsulitis: Adhesive capsulitis, also known as frozen shoulder, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. Shoulder MRI can detect the signs of adhesive capsulitis, including thickening of the joint capsule and adhesions between the capsule and the surrounding soft tissues.
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that affects the cartilage and bone of the shoulder joint, leading to pain and stiffness. Shoulder MRI can detect the signs of osteoarthritis, including cartilage loss, subchondral sclerosis, and osteophyte formation.
- Bone Marrow Edema: Bone marrow edema is a condition characterized by increased signal intensity in the bone marrow on T2-weighted images, which can occur due to various conditions, including fractures, osteonecrosis, and inflammation. Shoulder MRI can detect bone marrow edema, which appears as a region of high signal intensity in the bone marrow.
- Tendinosis: Tendinosis is a condition characterized by degenerative changes in the tendons, leading to pain and weakness. Shoulder MRI can detect the signs of tendinosis, including thickening of the tendon, increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images, and calcifications.
- Subacromial Bursitis: Subacromial bursitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the subacromial bursa, which can occur due to various conditions, including shoulder impingement and rotator cuff tears. Shoulder MRI can detect the signs of subacromial bursitis, including thickening of the bursa and increased fluid signal intensity on T2-weighted images.
- Labral Cysts: Labral cysts are fluid-filled lesions that can occur in the labrum, leading to pain and weakness. Shoulder MRI can detect labral cysts, which appear as a fluid-filled lesion in the labrum, with or without communication with the joint.
- Glenohumeral Instability: Glenohumeral instability is a condition characterized by excessive movement of the humeral head in the glenoid fossa, leading to pain and weakness. Shoulder MRI can detect the signs of glenohumeral instability, including a Hill-Sachs lesion, which is a compression fracture of the humeral head, and a Bankart lesion, which is a fracture of the glenoid rim.
Conclusion
In conclusion, shoulder MRI is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides detailed images of the shoulder joint, helping clinicians to identify and diagnose a range of conditions. The 10 insights outlined in this article are essential for accurate diagnosis using shoulder MRI, and highlight the importance of technical considerations, such as the use of a high-field strength MRI machine and a dedicated shoulder coil. By understanding these insights, clinicians can improve their diagnostic accuracy and provide effective treatment for patients with shoulder conditions.
What is the most common indication for shoulder MRI?
+The most common indication for shoulder MRI is to evaluate shoulder pain and weakness, particularly in patients with suspected rotator cuff tears or labral tears.
What is the difference between T1-weighted and T2-weighted images in shoulder MRI?
+T1-weighted images provide anatomical detail, while T2-weighted images are fluid-sensitive and provide information about the presence of edema or inflammation.
Can shoulder MRI detect osteoarthritis?
+Yes, shoulder MRI can detect the signs of osteoarthritis, including cartilage loss, subchondral sclerosis, and osteophyte formation.



