12+ Ace Inhibitor Secrets For Sarcoidosis Management Success
Sarcoidosis is a complex and multifaceted disease that affects various parts of the body, including the lungs, skin, and eyes. Managing the condition requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates medication, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing monitoring. One crucial aspect of sarcoidosis management is the use of ACE inhibitors, which have been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the world of ACE inhibitors and explore their role in sarcoidosis management, highlighting 12+ secrets to success.
Introduction to ACE Inhibitors

ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, are a class of medications that have been widely used to treat conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy. They work by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that can exacerbate inflammation and tissue damage. In the context of sarcoidosis, ACE inhibitors have been found to be particularly useful in reducing inflammation and improving lung function.
How ACE Inhibitors Work in Sarcoidosis
The exact mechanism by which ACE inhibitors exert their effects in sarcoidosis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and the reduction of oxidative stress. Studies have shown that ACE inhibitors can decrease the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta, which are elevated in sarcoidosis patients. Additionally, ACE inhibitors have been found to enhance the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, which can help to mitigate the inflammatory response.
| ACE Inhibitor | Dosage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Enalapril | 10-20 mg | Once daily |
| Lisinopril | 20-40 mg | Once daily |
| Captopril | 25-50 mg | Twice daily |
12+ Ace Inhibitor Secrets for Sarcoidosis Management Success

While ACE inhibitors can be a valuable addition to sarcoidosis treatment, there are several secrets to success that patients and healthcare providers should be aware of. These include:
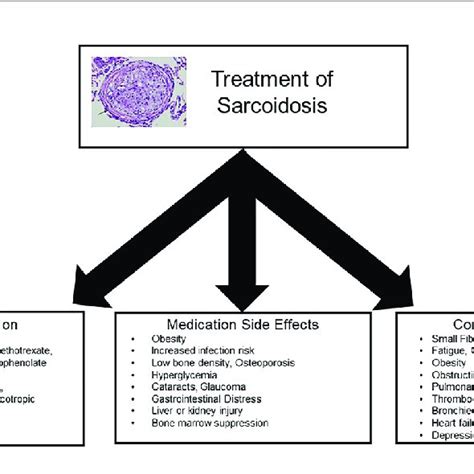
- Monitoring kidney function: ACE inhibitors can affect kidney function, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal disease. Regular monitoring of kidney function is essential to ensure safe and effective use.
- Managing potassium levels: ACE inhibitors can increase potassium levels, which can be problematic for patients with kidney disease or those taking other medications that affect potassium levels.
- Watching for cough: ACE inhibitors can cause a dry, persistent cough in some patients, which can be a challenge for those with sarcoidosis who may already be experiencing respiratory symptoms.
- Combining with other medications: ACE inhibitors can be used in combination with other medications, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, to enhance their effects and minimize side effects.
- Adjusting dosage: The dosage of ACE inhibitors may need to be adjusted based on individual patient response and medical history.
- Monitoring blood pressure: ACE inhibitors can lower blood pressure, which can be beneficial for patients with hypertension but may require careful monitoring in those with hypotension.
- Evaluating lung function: Regular assessment of lung function is essential to determine the effectiveness of ACE inhibitors in sarcoidosis patients.
- Considering alternative options: In some cases, alternative medications or therapies may be necessary for patients who do not respond to ACE inhibitors or experience significant side effects.
- Providing patient education: Patients should be educated on the proper use of ACE inhibitors, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to treatment.
- Encouraging lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet, can complement the effects of ACE inhibitors and improve overall health.
- Monitoring for side effects: Regular monitoring for side effects, such as dizziness, headache, and fatigue, is essential to ensure safe and effective use of ACE inhibitors.
- Collaborating with healthcare providers: Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their condition, adjust treatment as needed, and address any concerns or questions.
What are the most common side effects of ACE inhibitors in sarcoidosis patients?
+The most common side effects of ACE inhibitors in sarcoidosis patients include cough, dizziness, headache, and fatigue. However, these side effects are typically mild and temporary, and can be managed with dose adjustments or alternative medications.
Can ACE inhibitors be used in combination with other medications for sarcoidosis?
+Yes, ACE inhibitors can be used in combination with other medications, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, to enhance their effects and minimize side effects. However, patients should be closely monitored for potential interactions and side effects.
How long does it take to see the effects of ACE inhibitors in sarcoidosis patients?
+The effects of ACE inhibitors in sarcoidosis patients can be seen within several weeks to months of treatment. However, the full benefits of ACE inhibitors may take longer to develop, and patients should be patient and consistent with their treatment regimen.



