Cellulitis Remedies Revealed: Natural Relief

Cellulitis, a common bacterial skin infection, affects millions of people worldwide, causing redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. While conventional treatments often involve antibiotics, many individuals are turning to natural remedies to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. In this article, we will delve into the world of cellulitis remedies, exploring the most effective natural treatments and providing expert insights on how to manage this condition.
Natural Remedies for Cellulitis: An Overview

Before we dive into the specifics of natural remedies, it’s essential to understand the causes and symptoms of cellulitis. This infection occurs when bacteria, typically Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, enter the skin through a cut, scratch, or other opening. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. Natural remedies can help alleviate these symptoms, reducing the need for antibiotics and promoting a faster recovery.
Top Natural Remedies for Cellulitis
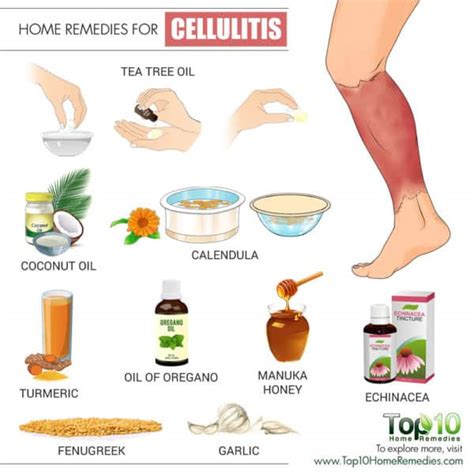
Several natural remedies have been proven effective in managing cellulitis symptoms. Some of the most popular and researched remedies include:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antimicrobial properties, tea tree oil can help combat bacterial infections and reduce inflammation.
- Echinacea: This herb is believed to boost the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and promote healing.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe and calm the skin, reducing redness and swelling.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil’s antimicrobial properties can help combat bacterial infections, while its moisturizing properties can help soothe and hydrate the skin.
| Remedy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Tea Tree Oil | Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory |
| Echinacea | Immune system booster, anti-inflammatory |
| Aloe Vera | Anti-inflammatory, soothing, moisturizing |
| Coconut Oil | Antimicrobial, moisturizing, anti-inflammatory |

Managing Cellulitis: Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
While natural remedies can help alleviate symptoms, making lifestyle changes and taking preventative measures can help manage cellulitis and reduce the risk of future infections. Some tips include:
- Keeping the skin clean and dry: Regularly washing the skin with soap and water can help prevent bacterial growth and reduce the risk of infection.
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing: Tight clothing can irritate the skin, increasing the risk of infection. Wearing loose, comfortable clothing can help reduce irritation and promote healing.
- Avoiding sharing personal items: Sharing personal items, such as towels or clothing, can spread bacteria and increase the risk of infection.
Nutritional Changes for Cellulitis Management
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help boost the immune system and promote healing. Some foods that may be beneficial for cellulitis management include:
- Leafy greens: Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are rich in antioxidants and can help reduce inflammation.
- Berries: Berries, such as blueberries and raspberries, are rich in antioxidants and can help boost the immune system.
- Fatty fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
What are the most common causes of cellulitis?
+Cellulitis is typically caused by bacterial infections, such as Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, which enter the skin through a cut, scratch, or other opening.
How can I prevent cellulitis?
+Preventing cellulitis involves keeping the skin clean and dry, wearing loose, comfortable clothing, and avoiding sharing personal items. A healthy diet and regular exercise can also help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of infection.
What are the most effective natural remedies for cellulitis?
+Some of the most effective natural remedies for cellulitis include tea tree oil, echinacea, aloe vera, and coconut oil. These remedies can help alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.



