Chain Reaction

The concept of a "chain reaction" has been a topic of interest across various scientific disciplines, from chemistry and physics to ecology and economics. At its core, a chain reaction refers to a series of events where each event triggers the next, often leading to a cascade of consequences. This phenomenon can be observed in both natural and human-made systems, showcasing its versatility and significance.
Understanding Chain Reactions

A chain reaction typically involves an initial event or action that sets off a sequence of subsequent events. This can occur in various contexts, such as chemical reactions, nuclear fission, ecological systems, and even social and economic phenomena. The key characteristic of a chain reaction is that each event is triggered by the previous one, creating a continuous chain of cause-and-effect relationships.
Chemical Chain Reactions
In chemistry, chain reactions are a type of chemical reaction where a reactive molecule or free radical initiates a series of subsequent reactions. This process continues until the reactants are consumed or the reaction is terminated. An example of a chemical chain reaction is the combustion of gasoline in a car engine. The initial spark ignites the gasoline, which then reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light, sustaining the combustion process.
| Chemical Reaction | Description |
|---|---|
| Combustion of Gasoline | Initial spark ignites gasoline, which reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light. |
| Polymerization | A monomer reacts with another monomer to form a dimer, which then reacts with another monomer to form a trimer, and so on. |

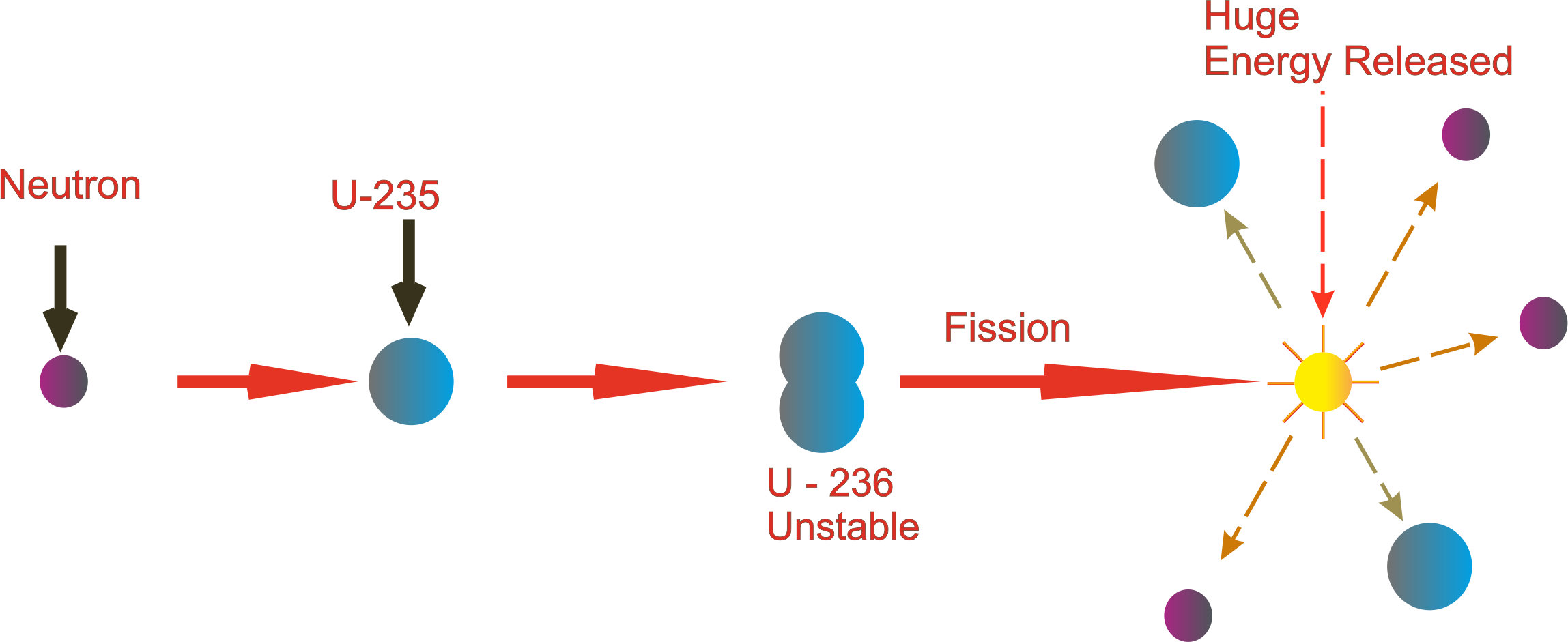
Nuclear Chain Reactions
Nuclear chain reactions occur when an atomic nucleus undergoes a fission reaction, releasing neutrons that then collide with other nuclei, causing them to undergo fission as well. This process can lead to a rapid increase in the number of fission reactions, potentially resulting in a nuclear explosion. The controlled nuclear chain reaction is the principle behind nuclear power plants, where the heat generated by fission is used to produce steam and drive a turbine.
The efficiency and safety of nuclear power plants rely heavily on the careful management of nuclear chain reactions. By controlling the rate of fission reactions, operators can ensure a stable and efficient production of energy.
Ecological and Social Chain Reactions
Chain reactions are not limited to physical or chemical systems; they can also occur in ecological and social contexts. In ecology, the loss of a key species can have a ripple effect throughout an ecosystem, leading to changes in population dynamics and potentially even extinctions. Similarly, in social systems, a change in social norms or policies can trigger a chain reaction of subsequent changes in behavior and attitudes.
Economic Chain Reactions
In economics, a chain reaction can occur when a change in one market or sector has a ripple effect on other markets or sectors. For example, a decline in housing prices can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which can then affect the overall economy. Understanding these chain reactions is crucial for policymakers and economists to predict and mitigate the effects of economic shocks.
- A decline in housing prices can lead to a decrease in consumer spending.
- A decrease in consumer spending can affect the overall economy.
- Economic chain reactions can have far-reaching consequences, making it essential to monitor and analyze market trends.
Conclusion

In conclusion, chain reactions are a fundamental phenomenon that can be observed in various scientific disciplines, from chemistry and physics to ecology and economics. Understanding the mechanisms and consequences of chain reactions is crucial for predicting and mitigating their effects, whether in natural systems or human-made structures.
What is a chain reaction?
+A chain reaction is a series of events where each event triggers the next, often leading to a cascade of consequences.
Can chain reactions occur in social systems?
+Yes, chain reactions can occur in social systems, such as changes in social norms or policies that trigger subsequent changes in behavior and attitudes.
How are chain reactions managed in nuclear power plants?
+Chain reactions in nuclear power plants are managed by controlling the rate of fission reactions, ensuring a stable and efficient production of energy.



