Factor Vii Activity Levels: Understanding Risks
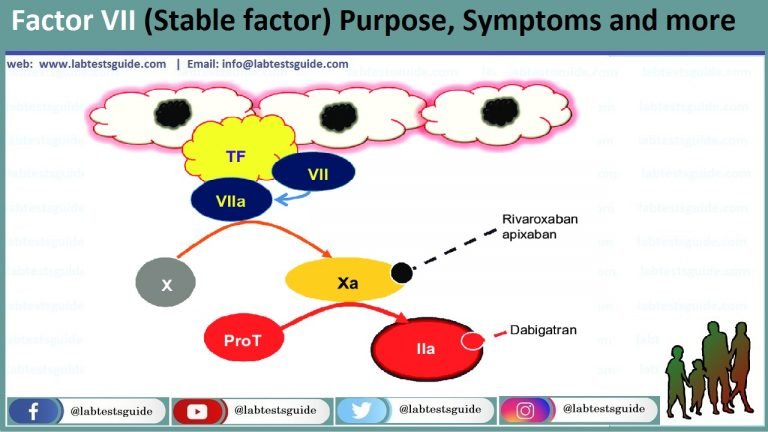
Factor VII, also known as proconvertin, is a vitamin K-dependent clotting factor produced in the liver. It plays a crucial role in the coagulation cascade, particularly in the initiation of blood clot formation. Factor VII activity levels are essential in assessing the risk of bleeding or thrombotic disorders. In this article, we will delve into the significance of factor VII activity levels, the risks associated with abnormal levels, and the clinical implications of these findings.
Introduction to Factor VII Activity Levels

Factor VII is a serine protease that activates factor X, which in turn leads to the formation of thrombin and eventually fibrin clot. The activity level of factor VII is measured in units per milliliter (U/mL) or as a percentage of normal activity. A normal factor VII activity level typically ranges from 50% to 150% of the normal reference value. Variations in factor VII activity levels can be influenced by genetic factors, age, sex, and lifestyle habits such as smoking and diet.
Genetic Factors Influencing Factor VII Activity Levels
Genetic variations, particularly in the F7 gene, can affect factor VII activity levels. Some individuals may have a variant of the F7 gene that results in reduced factor VII activity, increasing the risk of bleeding disorders. Conversely, other genetic variants may lead to elevated factor VII activity, which can increase the risk of thrombotic events. Understanding the genetic basis of factor VII activity levels is essential in identifying individuals at risk and providing personalized management strategies.
| Factor VII Activity Level | Risk Association |
|---|---|
| Low (<50% of normal) | Bleeding disorders |
| High (>150% of normal) | Thrombotic events |
| Normal (50-150% of normal) | No increased risk |

Clinical Implications of Abnormal Factor VII Activity Levels

Abnormal factor VII activity levels can have significant clinical implications. Individuals with low factor VII activity levels may experience bleeding complications, such as easy bruising, nosebleeds, or heavy menstrual bleeding. On the other hand, those with high factor VII activity levels may be at increased risk of thrombotic events, such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Accurate measurement and interpretation of factor VII activity levels are crucial in diagnosing and managing these conditions.
Risks Associated with Elevated Factor VII Activity Levels
Elevated factor VII activity levels have been linked to an increased risk of thrombotic events. The mechanism underlying this association is thought to involve the enhanced activation of factor X and the subsequent formation of thrombin and fibrin clot. Individuals with high factor VII activity levels may be at increased risk of developing arterial thrombosis, including myocardial infarction and stroke. Additionally, elevated factor VII activity levels have been associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Management Strategies for Abnormal Factor VII Activity Levels
Management strategies for abnormal factor VII activity levels depend on the underlying cause and the associated clinical risks. Individuals with low factor VII activity levels may require replacement therapy with factor VII concentrates to prevent or treat bleeding complications. Those with high factor VII activity levels may benefit from anticoagulant therapy to reduce the risk of thrombotic events. In addition to these pharmacological interventions, lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and regular exercise, may help mitigate the risks associated with abnormal factor VII activity levels.
What is the normal range for factor VII activity levels?
+The normal range for factor VII activity levels is typically between 50% and 150% of the normal reference value.
What are the risks associated with low factor VII activity levels?
+Individuals with low factor VII activity levels may experience bleeding complications, such as easy bruising, nosebleeds, or heavy menstrual bleeding.
How can elevated factor VII activity levels be managed?
+Management strategies for elevated factor VII activity levels may include anticoagulant therapy and lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and regular exercise.



