Gastric Ulcer Guide: Symptoms And Treatment
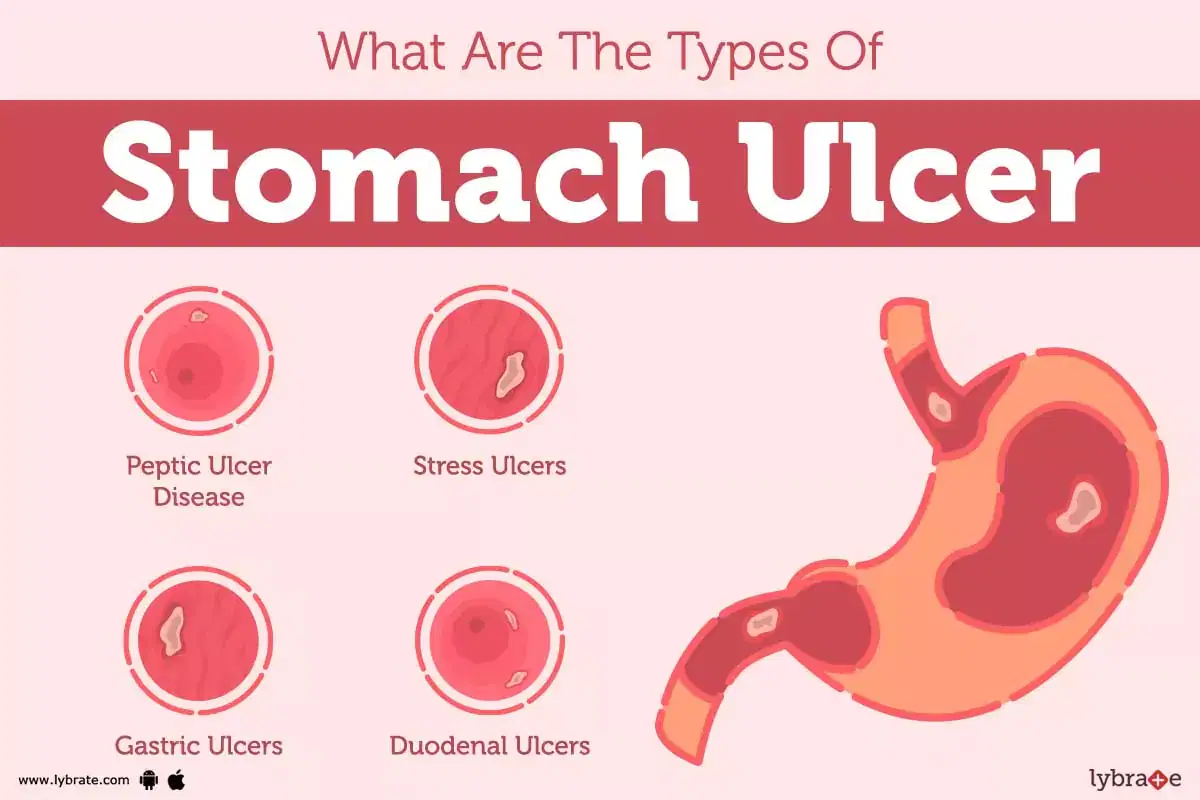
Gastric ulcers, also known as stomach ulcers, are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach. They are a type of peptic ulcer, which can also occur in the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. Gastric ulcers are a common health issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for gastric ulcers, providing a comprehensive guide for those affected by this condition.
Understanding Gastric Ulcers

Gastric ulcers occur when the lining of the stomach is damaged, allowing stomach acid to come into contact with the underlying tissue. This can cause pain, bleeding, and other complications. The most common cause of gastric ulcers is infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Other factors that can contribute to the development of gastric ulcers include long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), stress, and a poor diet.
Symptoms of Gastric Ulcers
The symptoms of gastric ulcers can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Abdominal pain, typically in the upper abdomen
- Bloating and discomfort after eating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Blood in the stool or black, tarry stools
In some cases, gastric ulcers can cause more severe symptoms, such as vomiting blood or experiencing severe abdominal pain. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Causes and Risk Factors
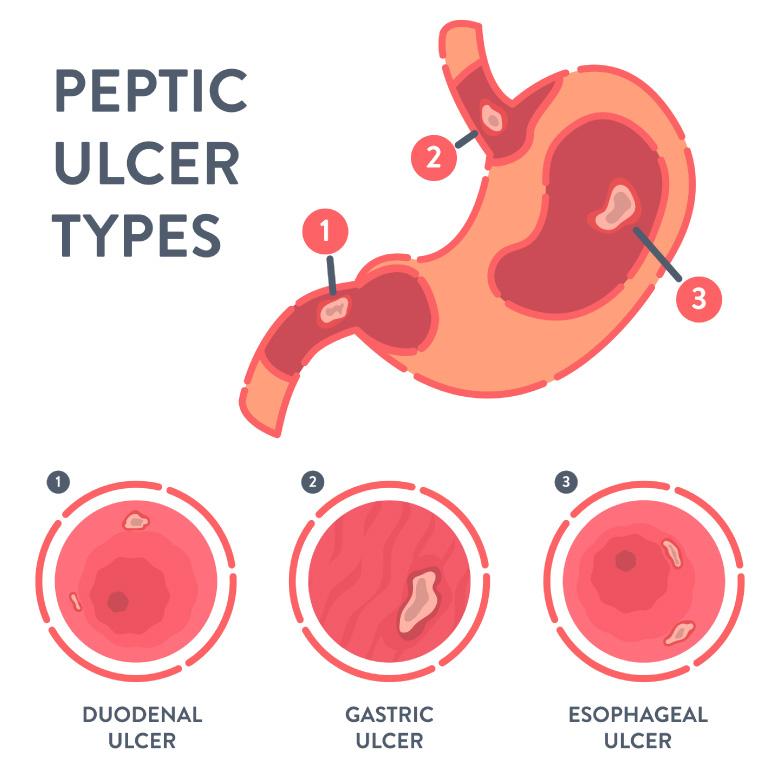
As mentioned earlier, the most common cause of gastric ulcers is infection with H. pylori. This bacterium can be spread through contaminated food, water, or close contact with an infected person. Other risk factors for developing gastric ulcers include:
- Long-term use of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or aspirin
- Stress, which can increase the production of stomach acid
- A poor diet, high in processed and fatty foods
- Smoking, which can reduce blood flow to the stomach and increase the risk of ulcers
Understanding the causes and risk factors for gastric ulcers can help you take steps to prevent them and reduce your risk of developing this condition.
Treatment Options for Gastric Ulcers
Treatment for gastric ulcers typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. The primary goals of treatment are to:
- Heal the ulcer
- Reduce symptoms
- Prevent complications, such as bleeding or perforation
Medications used to treat gastric ulcers include:
- Antibiotics, to treat H. pylori infection
- Acid reducers, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or histamine-2 (H2) blockers
- Protective medications, such as sucralfate or misoprostol, to protect the stomach lining
Lifestyle changes that can help manage gastric ulcers include:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet
- Avoiding spicy or fatty foods
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing
- Quitting smoking
Complications and Prevention
If left untreated, gastric ulcers can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Bleeding, which can be life-threatening
- Perforation, where the ulcer burrows through the stomach wall and into the abdominal cavity
- Obstruction, where the ulcer blocks the passage of food through the stomach
To prevent these complications, it is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of a gastric ulcer. Your doctor may recommend:
- Endoscopy, to visualize the stomach lining and diagnose the ulcer
- Blood tests, to check for H. pylori infection or anemia
- Stool tests, to check for blood or other abnormalities
| Medication | Dosage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Omeprazole | 20mg | Once daily |
| Amoxicillin | 500mg | Twice daily |
| Sucralfate | 1g | Four times daily |

What are the symptoms of a gastric ulcer?
+The symptoms of a gastric ulcer can include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and weight loss. In some cases, gastric ulcers can cause more severe symptoms, such as vomiting blood or experiencing severe abdominal pain.
How are gastric ulcers diagnosed?
+Gastric ulcers are typically diagnosed using a combination of endoscopy, blood tests, and stool tests. Endoscopy allows your doctor to visualize the stomach lining and diagnose the ulcer, while blood tests and stool tests can help identify H. pylori infection or anemia.
Can gastric ulcers be prevented?
+Yes, gastric ulcers can be prevented by taking steps to reduce your risk factors. This includes eating a healthy, balanced diet, avoiding spicy or fatty foods, reducing stress, and quitting smoking. Additionally, taking medications as directed and following a treatment plan can help prevent complications.



