Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Protect Your Dog
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, commonly referred to as MRSA, is a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics. While it is a significant concern for human health, it can also affect dogs. As a dog owner, it is essential to understand the risks associated with MRSA and take steps to protect your pet. In this article, we will delve into the world of MRSA, its causes, symptoms, and prevention methods, providing you with the knowledge you need to keep your dog safe.
What is MRSA?

MRSA is a strain of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria that has developed resistance to methicillin, a type of antibiotic. This resistance makes it challenging to treat infections caused by MRSA, as it can withstand the effects of many commonly used antibiotics. MRSA can cause a range of infections, from mild skin infections to life-threatening diseases such as pneumonia and sepsis.
How do dogs get MRSA?
Dogs can become infected with MRSA through various means, including:
- Direct contact with an infected person or animal
- Indirect contact with contaminated surfaces, equipment, or food
- Contaminated water or soil
Dogs that are more susceptible to MRSA infections include those with compromised immune systems, skin conditions, or underlying health issues. Additionally, dogs that frequent areas with high levels of MRSA, such as veterinary clinics or dog parks, may be at increased risk of infection.
Symptoms of MRSA in Dogs

The symptoms of MRSA in dogs can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Redness, swelling, and discharge around the affected area
- Pus-filled lesions or abscesses
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
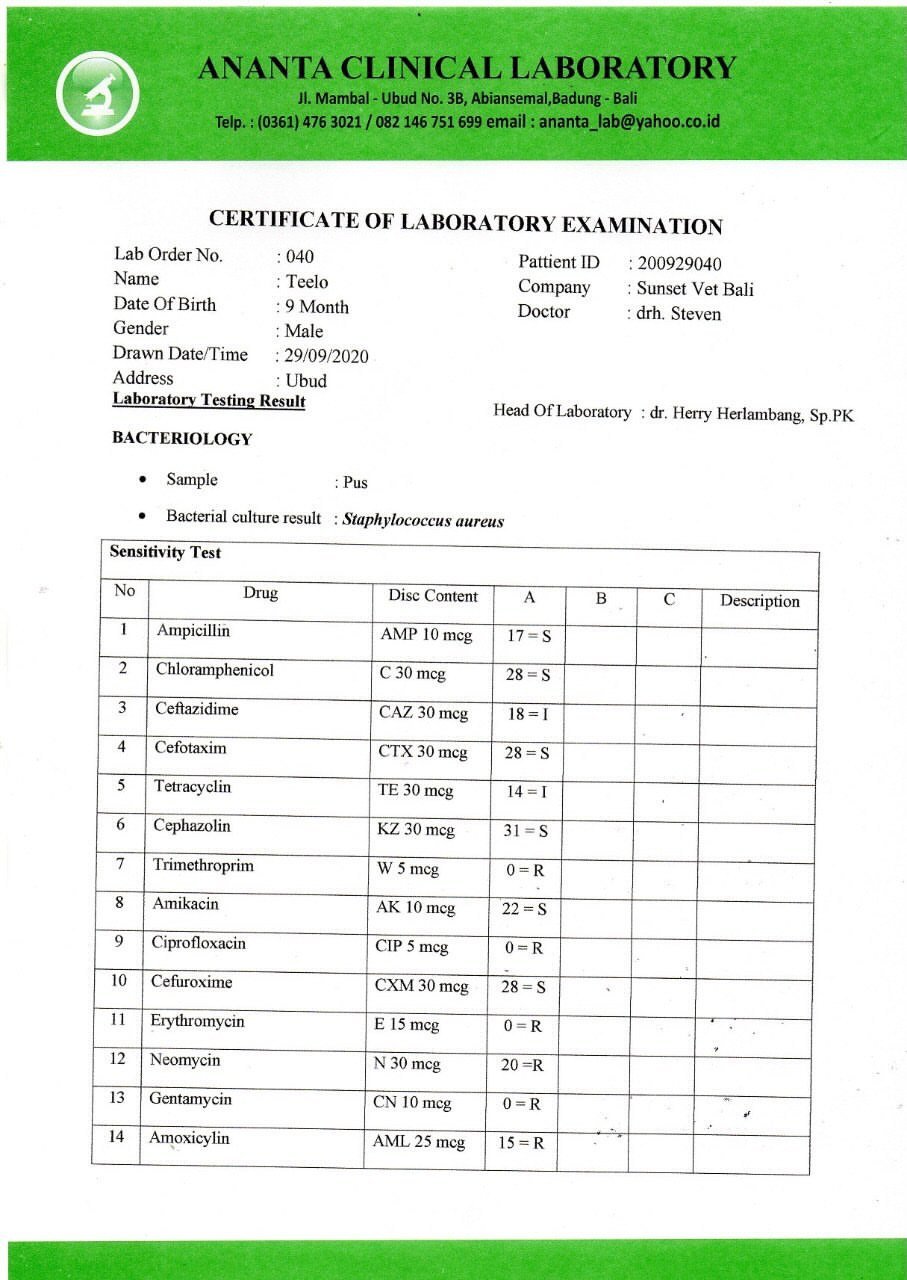
If you suspect that your dog has an MRSA infection, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention immediately. Your veterinarian will perform a physical examination, take a complete medical history, and conduct diagnostic tests, such as culturing the affected area, to confirm the presence of MRSA.
Treatment and Management of MRSA in Dogs
Treatment of MRSA in dogs typically involves a combination of antibiotics, wound care, and supportive therapy. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity and location of the infection, as well as the overall health of the dog. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide intensive care and monitoring.
It is essential to work closely with your veterinarian to ensure that your dog receives the best possible care. This may include:
- Administering antibiotics as directed
- Providing wound care and dressing changes
- Managing pain and discomfort
- Monitoring for signs of complications or worsening infection
Prevention is Key
Preventing MRSA infections in dogs requires a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and thoroughly
- Disinfecting surfaces, equipment, and food and water bowls regularly
- Avoiding contact with people or animals that may be infected with MRSA
- Keeping your dog’s environment clean and well-ventilated
- Ensuring your dog receives regular veterinary care and vaccinations
Additionally, you can take steps to reduce your dog’s risk of infection by:
- Avoiding areas with high levels of MRSA, such as veterinary clinics or dog parks, if possible
- Using a veterinarian-recommended antibacterial shampoo or soap on your dog
- Applying a topical antibiotic ointment to any cuts or wounds
MRSA and Dog Owners: What You Need to Know
As a dog owner, it is essential to understand the risks associated with MRSA and take steps to protect yourself and your pet. This includes:
- Wearing protective clothing, such as gloves and masks, when handling your dog or its environment
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and thoroughly
- Avoiding close contact with your dog if you have an open wound or are infected with MRSA
By taking these precautions, you can reduce the risk of transmission and help prevent the spread of MRSA.
| MRSA Prevention Methods | Efficacy |
|---|---|
| Practicing good hygiene | High |
| Disinfecting surfaces and equipment | High |
| Avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals | High |
| Using antibacterial shampoo or soap | Moderate |
| Applying topical antibiotic ointment | Moderate |

What is the most effective way to prevent MRSA in dogs?
+Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and thoroughly, is the most effective way to prevent MRSA in dogs. Additionally, disinfecting surfaces, equipment, and food and water bowls regularly can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Can dogs transmit MRSA to humans?
+Yes, dogs can transmit MRSA to humans. MRSA can be spread through direct contact with an infected dog or its environment, making it essential to practice good hygiene and take precautions when handling your dog or its surroundings.
How can I tell if my dog has an MRSA infection?
+If you suspect that your dog has an MRSA infection, look for symptoms such as redness, swelling, and discharge around the affected area, as well as fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek veterinary attention immediately.



