Mitochondrial Antibody Test: Diagnose Autoimmune Disorders

The mitochondrial antibody test is a diagnostic tool used to identify the presence of antibodies against mitochondrial antigens in the blood. These antibodies are often associated with autoimmune disorders, such as primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), where the immune system mistakenly attacks the mitochondria in liver cells, leading to inflammation and damage. In this article, we will delve into the world of mitochondrial antibody tests, exploring their significance, applications, and implications for diagnosing and managing autoimmune disorders.
Understanding Mitochondrial Antibodies
Mitochondrial antibodies are a type of autoantibody that targets the mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within cells. Under normal circumstances, the immune system recognizes and tolerates the body’s own cellular components, including mitochondria. However, in individuals with autoimmune disorders, the immune system mistakenly identifies mitochondrial antigens as foreign, triggering the production of mitochondrial antibodies. These antibodies can be detected in the blood using specialized tests, such as the mitochondrial antibody test.
Types of Mitochondrial Antibodies
There are several types of mitochondrial antibodies, each targeting specific antigens on the mitochondrial surface. The most common types include:
- Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMAs): These antibodies are most commonly associated with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and target the E2 component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC-E2) on the mitochondrial surface.
- Anti-M2 antibodies: These antibodies are often found in individuals with PBC and target the M2 antigen on the mitochondrial surface.
- Anti-M9 antibodies: These antibodies are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and target the M9 antigen on the mitochondrial surface.
Each type of mitochondrial antibody has a distinct clinical significance and is associated with specific autoimmune disorders. By detecting and characterizing these antibodies, healthcare professionals can diagnose and monitor the progression of autoimmune diseases.
Clinical Applications of Mitochondrial Antibody Tests

Mitochondrial antibody tests have several clinical applications, including:
- Diagnosing primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC): The presence of AMAs is a hallmark of PBC, and mitochondrial antibody tests are essential for diagnosing this condition.
- Monitoring disease progression: By monitoring the levels of mitochondrial antibodies over time, healthcare professionals can assess the effectiveness of treatment and disease progression.
- Differentiating between autoimmune disorders: Mitochondrial antibody tests can help differentiate between autoimmune disorders, such as PBC and SLE, which is essential for developing targeted treatment strategies.
Accurate diagnosis and monitoring of autoimmune disorders are critical for developing effective treatment plans and improving patient outcomes. Mitochondrial antibody tests play a vital role in this process, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care.
Interpreting Mitochondrial Antibody Test Results
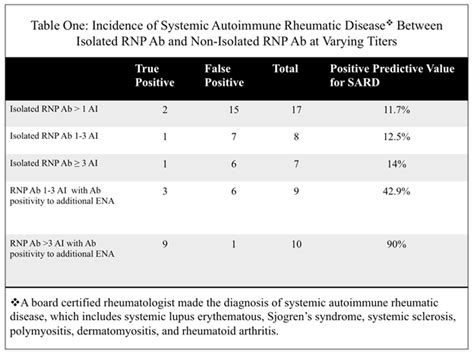
Interpreting mitochondrial antibody test results requires a thorough understanding of the clinical context and the specific antibody profiles. The following table summarizes the common mitochondrial antibody profiles and their clinical significance:
| Antibody Profile | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| AMA-positive | Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) |
| Anti-M2-positive | PBC or other autoimmune liver diseases |
| Anti-M9-positive | Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |
A comprehensive understanding of mitochondrial antibody profiles and their clinical significance is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune disorders.
Future Implications of Mitochondrial Antibody Tests
Advances in mitochondrial antibody testing have significant implications for the diagnosis and management of autoimmune disorders. Future research directions include:
- Developing more sensitive and specific testing methods
- Investigating the role of mitochondrial antibodies in other autoimmune disorders
- Exploring the potential of mitochondrial antibody tests for monitoring treatment response and disease progression
As our understanding of mitochondrial antibodies and their clinical significance continues to evolve, mitochondrial antibody tests will play an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and management of autoimmune disorders.
What is the primary use of mitochondrial antibody tests?
+Mitochondrial antibody tests are primarily used to diagnose and monitor autoimmune disorders, such as primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
What are the different types of mitochondrial antibodies?
+The most common types of mitochondrial antibodies include anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMAs), anti-M2 antibodies, and anti-M9 antibodies, each targeting specific antigens on the mitochondrial surface.
How are mitochondrial antibody test results interpreted?
+Mitochondrial antibody test results are interpreted based on the specific antibody profiles and their clinical significance, taking into account the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic findings.



