Multifocal Ventricular Ectopics: Expert Diagnosis Guide
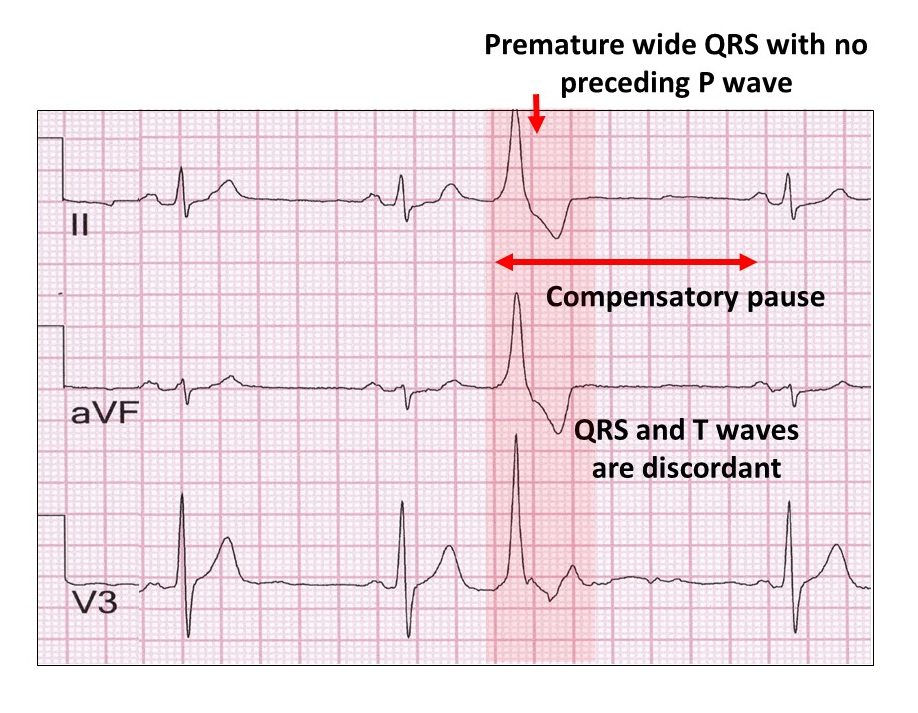
Multifocal ventricular ectopics (MVEs) are a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia, that originates in the ventricles, which are the lower chambers of the heart. These ectopic beats can occur in individuals with or without underlying heart disease and can be a source of concern for both patients and clinicians. In this article, we will delve into the world of MVEs, discussing their definition, causes, diagnosis, and management, with a focus on providing a comprehensive guide for expert diagnosis.
Definition and Classification

Multifocal ventricular ectopics are defined as three or more distinct morphologies of ventricular ectopic beats on a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). These ectopic beats can arise from different areas within the ventricles, hence the term “multifocal.” The classification of MVEs is based on the morphology of the ectopic beats, with different morphologies suggesting different origins within the ventricles. Understanding the morphology and origin of MVEs is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with multifocal ventricular ectopics may present with a variety of symptoms, including palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and in some cases, no symptoms at all. The clinical presentation can vary widely depending on the underlying heart disease, if any, and the frequency and complexity of the ectopic beats. Ventricular ectopics can be a benign finding in healthy individuals, but they can also be a sign of underlying cardiac pathology, such as cardiomyopathy or coronary artery disease.
| Category | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Benign | Isolated ectopics in healthy individuals |
| Pathological | Frequent ectopics in patients with underlying heart disease |

Causes and Risk Factors

The causes of multifocal ventricular ectopics can be diverse, ranging from benign conditions such as anxiety or stimulant use to more serious underlying heart diseases. Identifying the underlying cause is critical for guiding management and determining prognosis. Risk factors for developing MVEs include, but are not limited to, underlying heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of multifocal ventricular ectopics is primarily based on the electrocardiogram (ECG), which can show the characteristic multiple morphologies of ventricular ectopic beats. Additional diagnostic tests, such as echocardiography, cardiac MRI, or electrophysiological studies, may be necessary to evaluate the underlying cardiac structure and function. A thorough diagnostic approach is essential to identify any underlying cardiac pathology that may be contributing to the MVEs.
Given the complexity of diagnosing and managing multifocal ventricular ectopics, a multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and other healthcare professionals may be beneficial. Collaboration and communication among healthcare providers are key to ensuring that patients receive comprehensive and appropriate care.
Management and Treatment
The management of multifocal ventricular ectopics depends on the underlying cause, the frequency and complexity of the ectopic beats, and the presence of any symptoms or underlying heart disease. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and medical therapy to more invasive procedures such as catheter ablation in selected cases. Personalized treatment plans are essential, considering the unique needs and conditions of each patient.
Future Implications
As our understanding of multifocal ventricular ectopics and their underlying mechanisms evolves, so too do the potential therapeutic options. Ongoing research into the genetic, molecular, and electrophysiological basis of MVEs may lead to the development of new and more effective treatments. Furthermore, advances in diagnostic technologies, such as high-resolution ECG and advanced imaging techniques, will likely improve our ability to diagnose and manage these conditions.
What are multifocal ventricular ectopics?
+Multifocal ventricular ectopics are a type of abnormal heart rhythm that originates in the ventricles, characterized by three or more distinct morphologies of ventricular ectopic beats on an ECG.
How are multifocal ventricular ectopics diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of multifocal ventricular ectopics is primarily based on the electrocardiogram (ECG), which shows the characteristic multiple morphologies of ventricular ectopic beats. Additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to evaluate underlying cardiac structure and function.
What is the management of multifocal ventricular ectopics?
+The management of multifocal ventricular ectopics depends on the underlying cause, frequency, and complexity of the ectopic beats, and the presence of symptoms or underlying heart disease. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and medical therapy to catheter ablation in selected cases.



