Troponin Levels Decoded: Causes Revealed
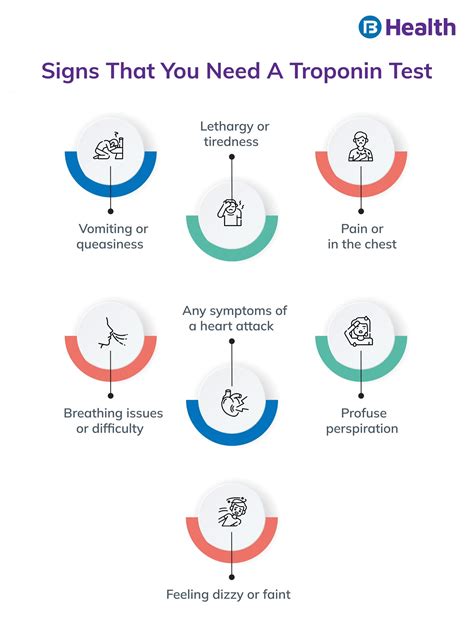
Troponin levels are a crucial indicator of cardiac health, and elevated levels can signal serious heart conditions. Troponin is a protein found in cardiac muscle cells, and its presence in the blood is a key marker of heart damage. In this article, we will delve into the causes of elevated troponin levels, exploring the various factors that contribute to this condition.
Understanding Troponin and Its Role in Cardiac Health
Troponin is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to the contractile apparatus of cardiac muscle cells. When cardiac cells are damaged, troponin is released into the bloodstream, where it can be detected using highly sensitive assays. The level of troponin in the blood is directly proportional to the extent of cardiac damage. Elevated troponin levels are a sensitive indicator of myocardial infarction (heart attack), but they can also be elevated in other conditions, such as myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure.
Clinical Significance of Troponin Levels
The clinical significance of troponin levels lies in their ability to diagnose and manage cardiac conditions. Cardiac biomarkers, such as troponin, are essential for early detection and treatment of heart disease. The troponin assay is a highly sensitive and specific test that can detect even minor elevations in troponin levels, allowing for early intervention and potentially improving patient outcomes. Table 1 summarizes the clinical significance of troponin levels.
| Troponin Level | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| Normal | No cardiac damage detected |
| Elevated | Cardiac damage detected, potentially indicating myocardial infarction or other cardiac conditions |
| Highly Elevated | Severe cardiac damage, potentially indicating large myocardial infarction or severe cardiac conditions |
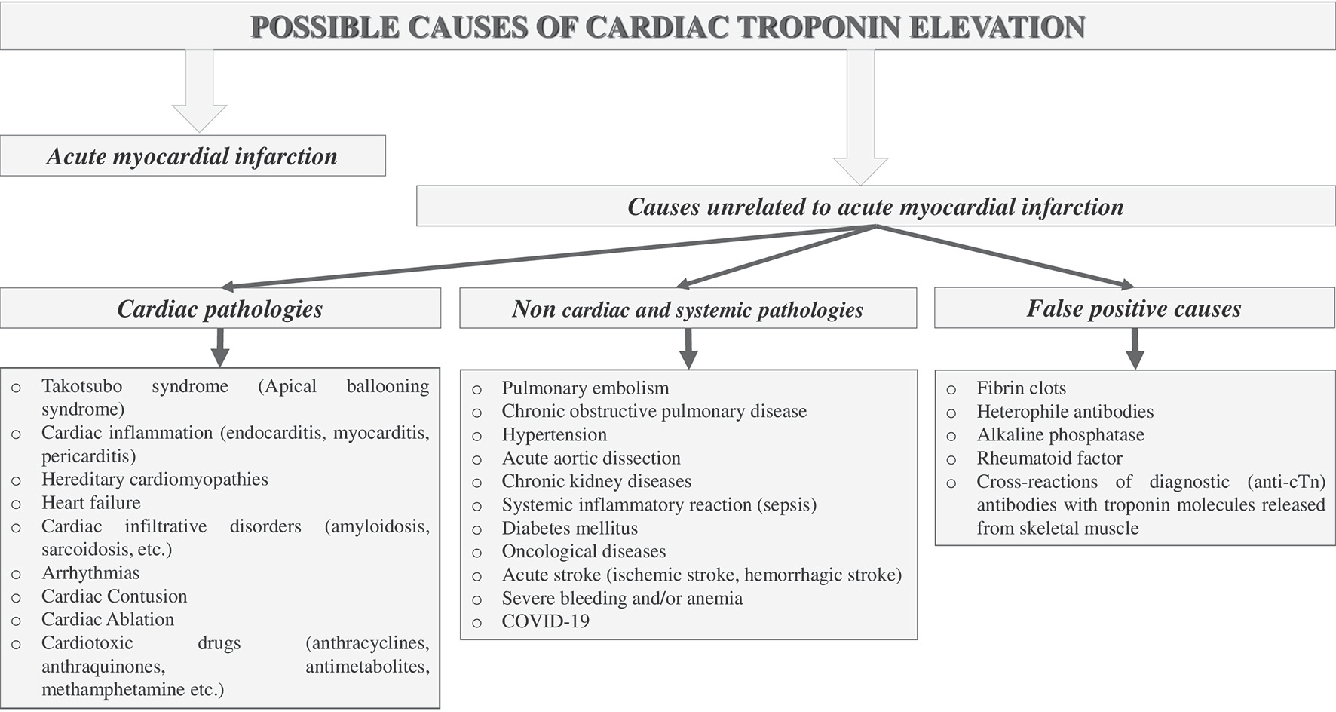
Causes of Elevated Troponin Levels
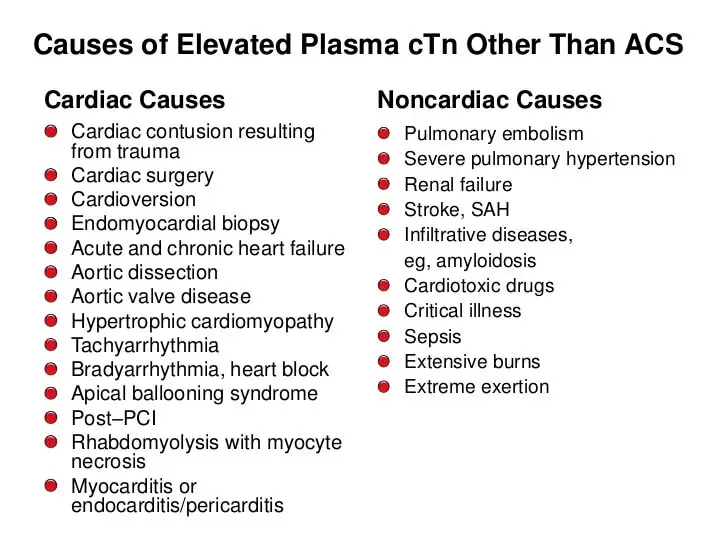
Elevated troponin levels can be caused by various factors, including cardiac and non-cardiac conditions. Myocardial infarction is the most common cause of elevated troponin levels, accounting for the majority of cases. Other cardiac conditions, such as myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure, can also elevate troponin levels. Non-cardiac conditions, such as sepsis, trauma, and renal failure, can also contribute to elevated troponin levels.
Cardiac Conditions that Elevate Troponin Levels
Cardiac conditions that elevate troponin levels include myocardial infarction, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Myocardial infarction is the most common cause of elevated troponin levels, and it occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing cardiac cells to die. Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, which can also elevate troponin levels. Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle, which can lead to elevated troponin levels. Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, and it can also elevate troponin levels.
Non-Cardiac Conditions that Elevate Troponin Levels
Non-cardiac conditions that elevate troponin levels include sepsis, trauma, and renal failure. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection becomes uncontrolled and causes widespread inflammation. Trauma can also elevate troponin levels, particularly if it involves chest trauma. Renal failure is a condition in which the kidneys are unable to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, and it can also contribute to elevated troponin levels.
Other Factors that Influence Troponin Levels
Other factors that influence troponin levels include age, sex, and renal function. Aging can affect troponin levels, as older adults may have higher troponin levels due to age-related changes in cardiac function. Sex can also influence troponin levels, as women may have lower troponin levels than men. Renal function is also an important factor, as impaired renal function can affect troponin levels.
What is the normal range for troponin levels?
+The normal range for troponin levels varies depending on the laboratory and the specific assay used. However, in general, troponin levels are considered normal if they are below 0.01-0.03 ng/mL.
What are the symptoms of elevated troponin levels?
+The symptoms of elevated troponin levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations.
How are elevated troponin levels treated?
+The treatment of elevated troponin levels depends on the underlying cause. In cases of myocardial infarction, treatment may involve medications to reduce cardiac workload, improve blood flow, and prevent further cardiac damage. In cases of non-cardiac conditions, treatment may involve addressing the underlying condition, such as sepsis or renal failure.



