Vbg Normal Ranges

The Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in medical practice to assess various components of the blood. One of the key parameters measured in a CBC is the Venous Blood Gas (VBG) analysis, which provides crucial information about the patient's oxygenation status, acid-base balance, and ventilatory function. Understanding VBG normal ranges is essential for healthcare professionals to interpret results accurately and make informed clinical decisions.
Introduction to Venous Blood Gas Analysis

Venous Blood Gas (VBG) analysis is a diagnostic test that measures the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in venous blood. It is commonly used in emergency medicine, critical care, and anesthesiology to assess patients with respiratory or metabolic disorders. Unlike arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, which requires an arterial puncture, VBG analysis involves a venous puncture, making it a less invasive and potentially more comfortable procedure for patients.
Components of Venous Blood Gas Analysis
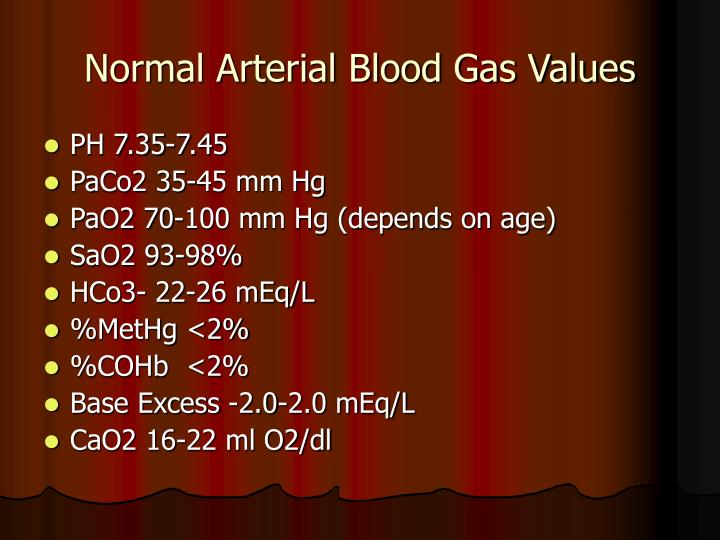
A typical VBG analysis includes measurements of pH, partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2), partial pressure of oxygen (pO2), bicarbonate (HCO3-), and base excess. These parameters help clinicians evaluate the acid-base status, oxygenation, and ventilatory function of the patient.
| Parameter | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35-7.45 |
| pCO2 (mmHg) | 40-50 |
| pO2 (mmHg) | 30-40 |
| HCO3- (mmol/L) | 22-28 |
| Base Excess (mmol/L) | -2 to +2 |

Interpretation of these parameters requires a comprehensive understanding of acid-base physiology and the clinical context in which the sample was collected. For instance, a low pH indicates acidosis, while a high pH suggests alkalosis. Similarly, elevated pCO2 levels may indicate respiratory acidosis, whereas decreased pCO2 levels may suggest respiratory alkalosis.
Clinical Applications of Venous Blood Gas Analysis
Venous Blood Gas analysis has a wide range of clinical applications, including the assessment of patients with suspected acid-base disturbances, evaluation of the effectiveness of ventilatory support, and monitoring of patients undergoing significant changes in their clinical status. It is particularly useful in situations where arterial blood sampling is not feasible or is associated with a high risk of complications.
Limitations and Considerations
While VBG analysis provides valuable information, it also has limitations. For example, pO2 levels in venous blood do not accurately reflect arterial oxygenation, as the pO2 in venous blood is significantly lower than in arterial blood due to the extraction of oxygen by tissues. Therefore, when assessing oxygenation status, arterial blood gas analysis or other specific tests like pulse oximetry may be more appropriate.
Moreover, the interpretation of VBG results requires consideration of the patient's hemodynamic status, as significant changes in cardiac output or peripheral resistance can affect the results. Clinicians must also be aware of potential pre-analytical errors, such as delays in sample analysis or inappropriate sample handling, which can lead to inaccurate results.
What is the primary difference between Venous Blood Gas (VBG) and Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) analysis?
+The primary difference between VBG and ABG analysis lies in the source of the blood sample. VBG analysis involves a venous puncture, whereas ABG analysis requires an arterial puncture. This difference affects the parameters measured and the clinical applications of each test.
How do you interpret a low pH in a Venous Blood Gas analysis?
+A low pH in a VBG analysis indicates acidosis. The cause of acidosis can be metabolic (e.g., diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis) or respiratory (e.g., respiratory depression leading to CO2 retention). Further evaluation and clinical correlation are necessary to determine the underlying cause.
What are the normal ranges for pCO2 and pO2 in a Venous Blood Gas analysis?
+The normal range for pCO2 in a VBG analysis is approximately 40-50 mmHg, and for pO2, it is about 30-40 mmHg. However, these ranges can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific analyzer used.



