Wasp Bite: Identify Symptoms & Treatments

The wasp bite is a common occurrence during the warmer months when these insects are most active. Unlike honeybees, wasps can sting multiple times, making their bites potentially more dangerous. It's essential to identify the symptoms of a wasp bite and understand the appropriate treatments to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Understanding Wasp Bites

Wasps, including paper wasps, yellowjackets, and hornets, are known for their aggressive behavior when threatened. Their stingers are smooth, allowing them to sting repeatedly without causing damage to themselves. The venom from a wasp bite contains a mixture of compounds that can cause pain, inflammation, and other systemic reactions. Most people will experience minor symptoms that can be treated at home, but some individuals may have severe allergic reactions that require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of a Wasp Bite
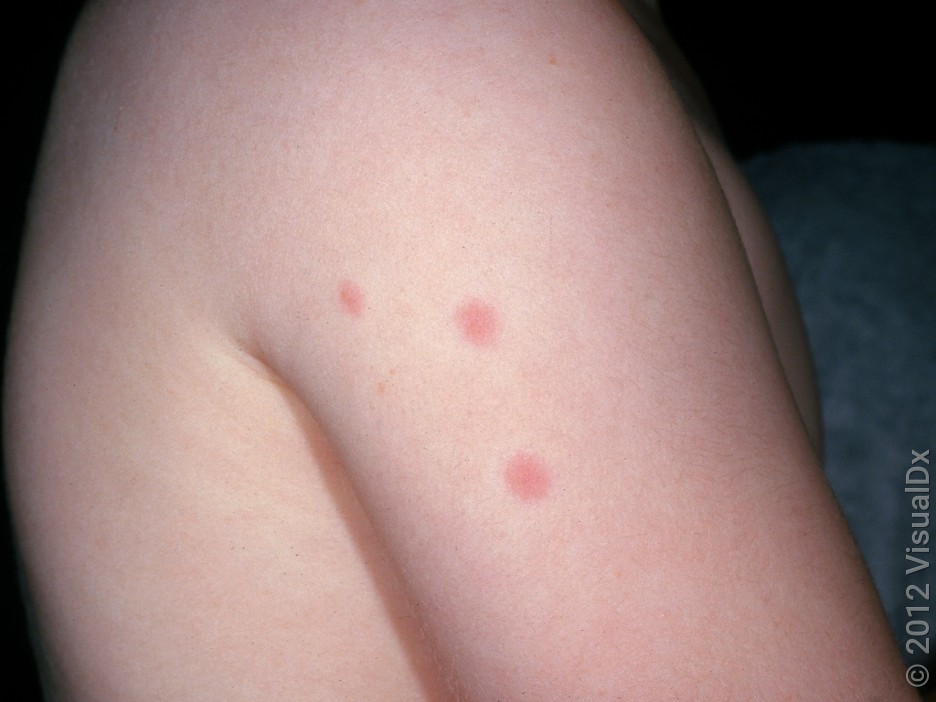
The symptoms of a wasp bite can vary from person to person, depending on the location of the bite, the number of stings, and the individual’s sensitivity to the venom. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling around the bite area
- Pain or a stinging sensation at the bite site
- Itching or burning sensation
- Minor bruising
In some cases, a wasp bite can trigger a severe allergic reaction, known as anaphylaxis. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
- Abdominal cramps
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
Treatments for Wasp Bites
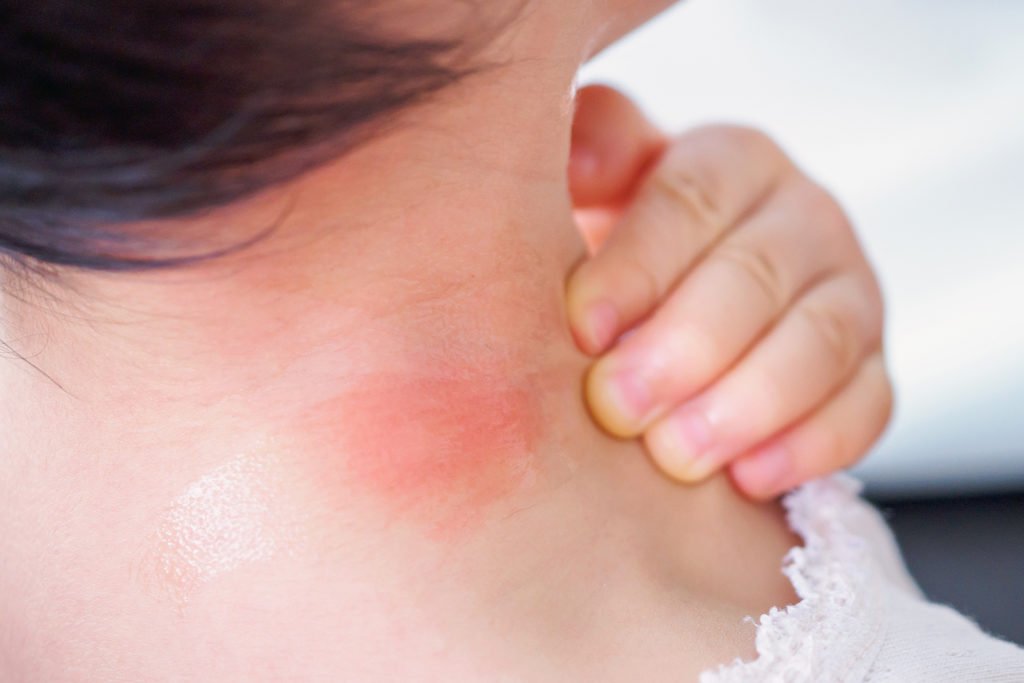
Mild wasp bites can be treated at home with basic first aid. For more severe reactions, medical attention may be necessary. Here are some common treatments for wasp bites:
For minor reactions:
- Wash the bite area with soap and water to prevent infection
- Apply a cold compress or an ice pack to reduce swelling
- Take an antihistamine or use a topical cream to relieve itching and inflammation
- Use a pain reliever, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to alleviate pain
For severe allergic reactions:
- Call emergency services or seek immediate medical attention
- Administer epinephrine using an EpiPen or other auto-injector, if available
- Loosen tight clothing and stay calm to help maintain breathing
Preventing Wasp Bites
While it’s impossible to completely avoid wasp bites, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of being stung:
- Avoid wearing perfumes, colognes, or other fragrances that may attract wasps
- Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, when outdoors
- Avoid eating sweet or fermented foods and drinks outdoors, as these can attract wasps
- Seal food and trash containers to prevent attracting wasps
- Avoid disturbing wasp nests or hives
| Reaction Type | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | Redness, swelling, pain, itching | First aid, antihistamines, pain relievers |
| Severe | Anaphylaxis, difficulty breathing, swelling | Emergency services, epinephrine, medical attention |
Understanding the symptoms and treatments for wasp bites can help you respond effectively in case of a sting. Remember to stay calm, seek medical attention if necessary, and take preventive measures to reduce the risk of being stung.
What is the difference between a wasp bite and a bee sting?
+A wasp bite and a bee sting are often used interchangeably, but they come from different insects. Bees have a barbed stinger that gets stuck in the skin, causing the bee to die after stinging. Wasps, on the other hand, have a smooth stinger and can sting multiple times.
How long do wasp bite symptoms last?
+Mild wasp bite symptoms typically last for a few hours to a few days. In some cases, redness and swelling may persist for up to a week. Severe allergic reactions, however, can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Can I prevent wasp bites by using insect repellents?
+While insect repellents can help deter wasps, they are not 100% effective. Wasps are attracted to sweet smells, food, and other scents, so it’s essential to take additional precautions, such as avoiding perfumes and sealing food containers, to reduce the risk of being stung.



