What Is Population Health Research? Improving Outcomes
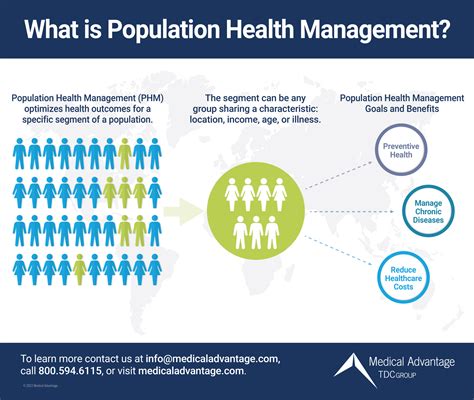
Population health research is a field of study that focuses on understanding the health outcomes and trends of specific populations, with the ultimate goal of improving health outcomes and reducing health disparities. This research involves analyzing data from various sources, including electronic health records, claims data, and community-based surveys, to identify patterns and trends in health outcomes. By examining the social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, education, and environmental factors, researchers can develop targeted interventions to address health inequities and improve population health.
Population health research is an interdisciplinary field that draws on theories and methods from epidemiology, sociology, psychology, and health services research. It involves collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and healthcare practitioners to design and implement effective interventions that promote health and well-being. The field is driven by the recognition that health outcomes are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including individual characteristics, social and environmental factors, and healthcare systems. By taking a comprehensive and nuanced approach to understanding population health, researchers can develop evidence-based solutions to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Key Concepts in Population Health Research

Several key concepts are central to population health research, including health disparities, which refer to differences in health outcomes and access to care among different population groups. Researchers also examine social determinants of health, such as housing, education, and employment, which can have a profound impact on health outcomes. Additionally, population health research often involves the use of geographic information systems (GIS) to analyze spatial patterns and trends in health outcomes. By mapping health outcomes and environmental factors, researchers can identify areas of high need and develop targeted interventions to address health inequities.
Methods and Approaches in Population Health Research
Population health research employs a range of methods and approaches, including quantitative and qualitative research designs. Quantitative research involves the analysis of large datasets to identify patterns and trends in health outcomes, while qualitative research involves in-depth interviews and focus groups to understand the experiences and perspectives of individuals and communities. Researchers also use mixed-methods approaches, which combine quantitative and qualitative methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of population health. Additionally, population health research often involves the use of community-based participatory research (CBPR) approaches, which involve collaboration with community members and stakeholders to design and implement research studies.
| Research Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Research | Analysis of large datasets to identify patterns and trends in health outcomes |
| Qualitative Research | In-depth interviews and focus groups to understand the experiences and perspectives of individuals and communities |
| Mixed-Methods Research | Combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to provide a comprehensive understanding of population health |
| Community-Based Participatory Research (CBPR) | Collaboration with community members and stakeholders to design and implement research studies |

Applications and Implications of Population Health Research

Population health research has a range of applications and implications, from informing healthcare policy and practice to guiding community-based interventions. By understanding the social determinants of health and identifying areas of high need, researchers can develop targeted interventions to address health inequities and improve health outcomes. Additionally, population health research can inform the development of value-based payment models, which reward healthcare providers for delivering high-quality, cost-effective care. By examining the relationships between healthcare systems, social determinants, and health outcomes, researchers can identify opportunities to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare services.
Future Directions in Population Health Research
Future directions in population health research include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze large datasets and identify patterns and trends in health outcomes. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of mobile health (mHealth) technologies to collect data and deliver interventions in real-time. By leveraging these emerging technologies, researchers can develop more effective and efficient interventions to improve population health and reduce healthcare costs. Furthermore, population health research is likely to play a critical role in addressing the social determinants of health, such as housing, education, and employment, which are increasingly recognized as key drivers of health outcomes.
- Use of AI and ML algorithms to analyze large datasets and identify patterns and trends in health outcomes
- Use of mHealth technologies to collect data and deliver interventions in real-time
- Addressing the social determinants of health, such as housing, education, and employment
- Developing targeted interventions to address health inequities and improve health outcomes
What is population health research?
+Population health research is a field of study that focuses on understanding the health outcomes and trends of specific populations, with the ultimate goal of improving health outcomes and reducing health disparities.
What are the key concepts in population health research?
+The key concepts in population health research include health disparities, social determinants of health, and geographic information systems (GIS).
What are the applications and implications of population health research?
+Population health research has a range of applications and implications, from informing healthcare policy and practice to guiding community-based interventions. It can inform the development of value-based payment models and identify opportunities to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare services.



