What Is Standard Deviation In Biology A Level? Made Easy
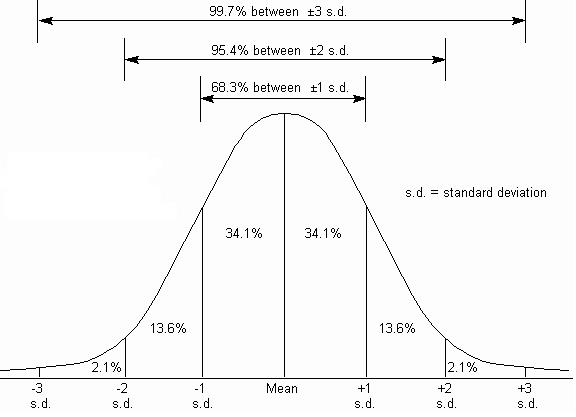
In biology, particularly at the A-level, understanding statistical measures is crucial for analyzing and interpreting data from experiments and research. One key concept in statistics is standard deviation, which is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. Standard deviation is used to quantify the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of data values. In the context of biology, it is essential for understanding the variability of biological data, such as the size of organisms, the concentration of substances, or the rate of biological processes.
What is Standard Deviation?

Standard deviation is a statistical measure that represents the spread or dispersion of a set of data from its mean value. It is calculated as the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean. The standard deviation is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma) and is usually expressed in the same units as the data. A low standard deviation indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean, while a high standard deviation indicates that the data points are spread out over a wider range of values.
Calculating Standard Deviation
The calculation of standard deviation involves several steps. First, the mean of the dataset is calculated. Then, the difference of each data point from the mean is calculated, and each difference is squared. The average of these squared differences is the variance. Finally, the standard deviation is calculated as the square root of the variance. The formula for calculating standard deviation is:
σ = √[(Σ(x - μ)^2) / (n - 1)]
where σ is the standard deviation, x is each data point, μ is the mean, and n is the number of data points.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| σ | Standard Deviation |
| μ | Mean |
| x | Each Data Point |
| n | Number of Data Points |

Importance of Standard Deviation in Biology

In biology, standard deviation is crucial for understanding the variability of biological data. It helps researchers to determine the reliability of their results and to identify any outliers or anomalies in the data. Standard deviation is also used to compare the variability of different datasets and to determine the significance of differences between them. For example, in a study on the effect of a new drug on the growth rate of bacteria, the standard deviation of the growth rates can be used to determine the variability of the response to the drug.
Furthermore, standard deviation is used in biology to calculate the confidence interval, which is a range of values within which a population parameter is likely to lie. The confidence interval is calculated using the standard deviation and the sample size, and it provides a measure of the precision of the estimate. In biology, confidence intervals are used to estimate population parameters, such as the mean size of a species or the proportion of individuals with a particular trait.
Real-World Applications of Standard Deviation in Biology
Standard deviation has numerous real-world applications in biology, including:
- Medical Research: Standard deviation is used to analyze the variability of patient responses to different treatments and to identify any outliers or anomalies in the data.
- Ecology: Standard deviation is used to study the variability of population sizes, species distributions, and ecosystem processes.
- Genetics: Standard deviation is used to analyze the variability of gene expression, genetic mutations, and population genetics.
In conclusion, standard deviation is a fundamental concept in statistics and biology, and it has numerous applications in real-world research. By understanding standard deviation, biologists can better analyze and interpret their data, and make more informed decisions about their research.
What is the formula for calculating standard deviation?
+The formula for calculating standard deviation is σ = √[(Σ(x - μ)^2) / (n - 1)], where σ is the standard deviation, x is each data point, μ is the mean, and n is the number of data points.
Why is standard deviation important in biology?
+Standard deviation is important in biology because it provides a measure of the variability of biological data, helps to identify outliers or anomalies, and is used to compare the variability of different datasets.
What is the difference between standard deviation and variance?
+Variance is the average of the squared differences from the mean, while standard deviation is the square root of the variance. Standard deviation is usually expressed in the same units as the data, while variance is expressed in squared units.



